Amazon Direct Fulfillment: A Vendor's Guide

Henriette Rasmussen
Amazon’s Direct Fulfillment (DF) program offers vendors a flexible alternative to traditional warehousing in its fulfillment centers. Instead of shipping goods to Amazon, vendors dispatch orders directly from their own warehouses to end customers, all under the Amazon banner.
This article explains how Direct Fulfillment works, outlines the key requirements for participation, and shows how vendors can manage processes, technology, and performance metrics effectively.
What is Direct Fulfillment?
With Direct Fulfillment (DF), vendors ship orders directly from their own warehouse to end customers. Unlike the Fulfilled-by-Amazon (FBA)-program, where Amazon manages storage and shipping, DF allows vendors to retain full control over their logistics.
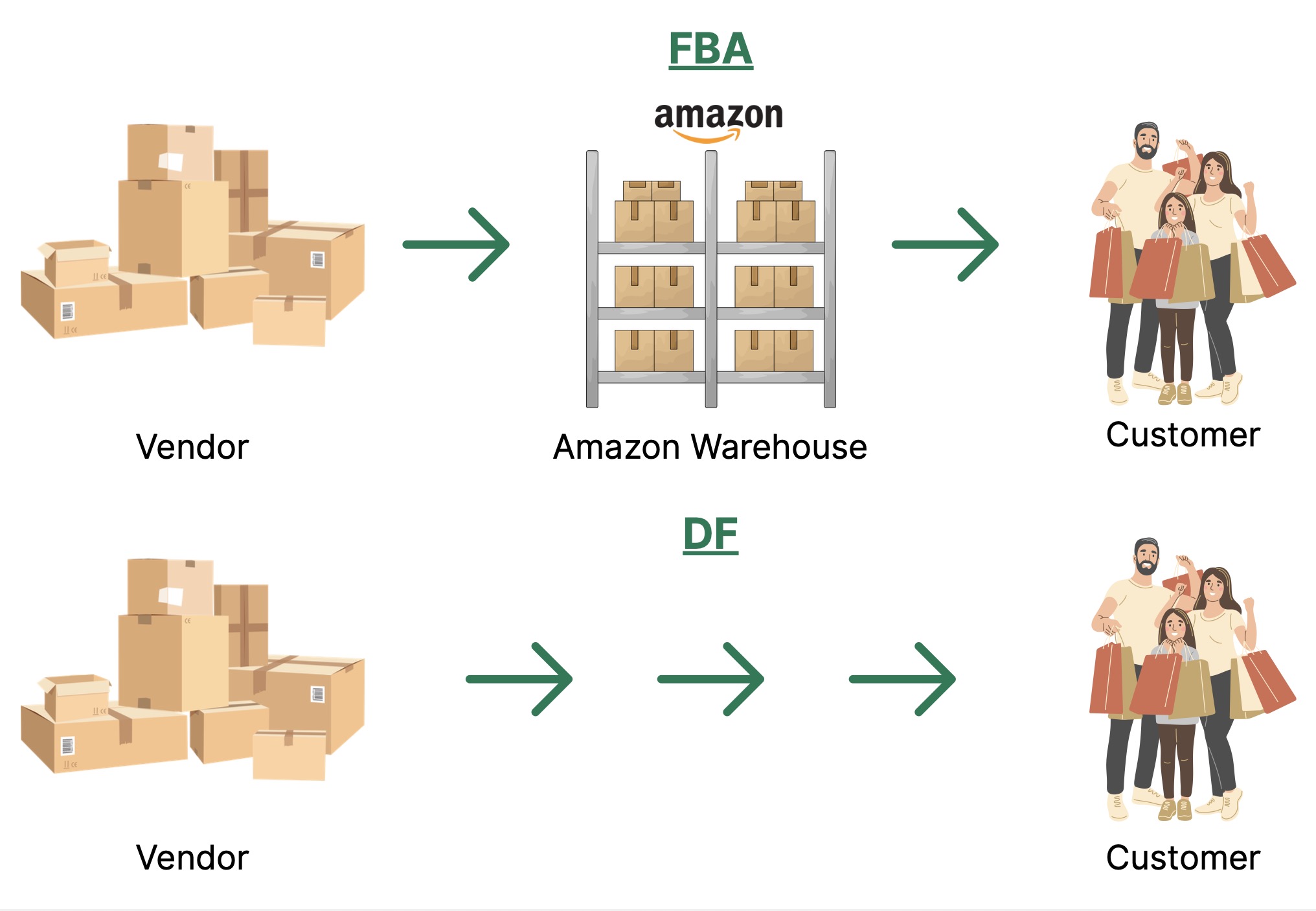
Amazon acts as the seller, provides prepaid shipping labels, and forwards orders. This allows vendors to benefit from the platform’s reach without giving up control of their own supply chain.
Core Advantages
- Faster Delivery: Shipping directly from your own warehouse enables shorter delivery times by eliminating the need for intermediate storage at Amazon.
- Full Inventory Control: Vendors manage their own stock and avoid overselling and cancellations through daily updates in Vendor Central.
- Transparent Management: Metrics like Expected Ship Date (ExSD) and Delivery Estimated Accuracy (DEA) allow you to proactively manage shipping processes and ensure customer satisfaction.
Fundamental Processes
Order processing takes place in Vendor Central under Orders > Direct Fulfillment Orders. Here, vendors manage all incoming DF orders from acceptance to shipment confirmation. The process includes the following steps:
- Order Acceptance: Amazon provides order details, including a prepaid shipping label (in PNG or ZPL format). Partial shipments are not allowed; incomplete orders must be canceled.
- Inventory Updates: Vendors must update their inventory daily in Vendor Central to prevent overselling and keep cancellation rates low.
- Shipment Preparation: The goods are picked and packed according to Amazon’s guidelines. Shipment usually must occur within 1-2 days to meet the Expected Ship Date (ExSD). The carrier specified by Amazon must be used.
- Print Shipping Label: The label is downloaded via Vendor Central or API/EDI. With “Amazon-Label-Only,” customer data is only visible on the label to ensure data privacy.
- Shipment Confirmation: After the package has been picked up by the carrier, the shipment is confirmed in Vendor Central (either manually or automatically). This is a prerequisite for invoicing.
Multi-Box Configuration
For products that require shipping in multiple packages, Direct Fulfillment offers a pre-configuration option. This ensures that the correct number of shipping labels is generated for future orders.
Configuration can be done in three ways:
- Bulk Update: Via a CSV file for multiple products at once.
- Individual Product Setting: Directly in the product details in Vendor Central.
- Order Level: Adjustments for a single, specific order.
Technical Integration and APIs
Amazon provides various interfaces for vendors to automate business processes (Vendor APIs). These include both Retail Vendor APIs (for catalog, orders, reports, etc.) and the Direct Fulfillment API Suite, which specifically covers the direct fulfillment order flow. This allows vendors to integrate the entire process – from order and shipping to invoicing – with minimal manual effort.
Direct Fulfillment API
The Direct Fulfillment API allows for the complete automation of the order cycle. Via the DF API, vendors can retrieve orders, confirm shipments, submit inventory, and exchange invoice documents.
The following diagram illustrates the typical workflow of an Amazon Direct Fulfillment process from a vendor’s perspective. The entire process is based on a series of API interactions between Amazon and the vendor’s system:
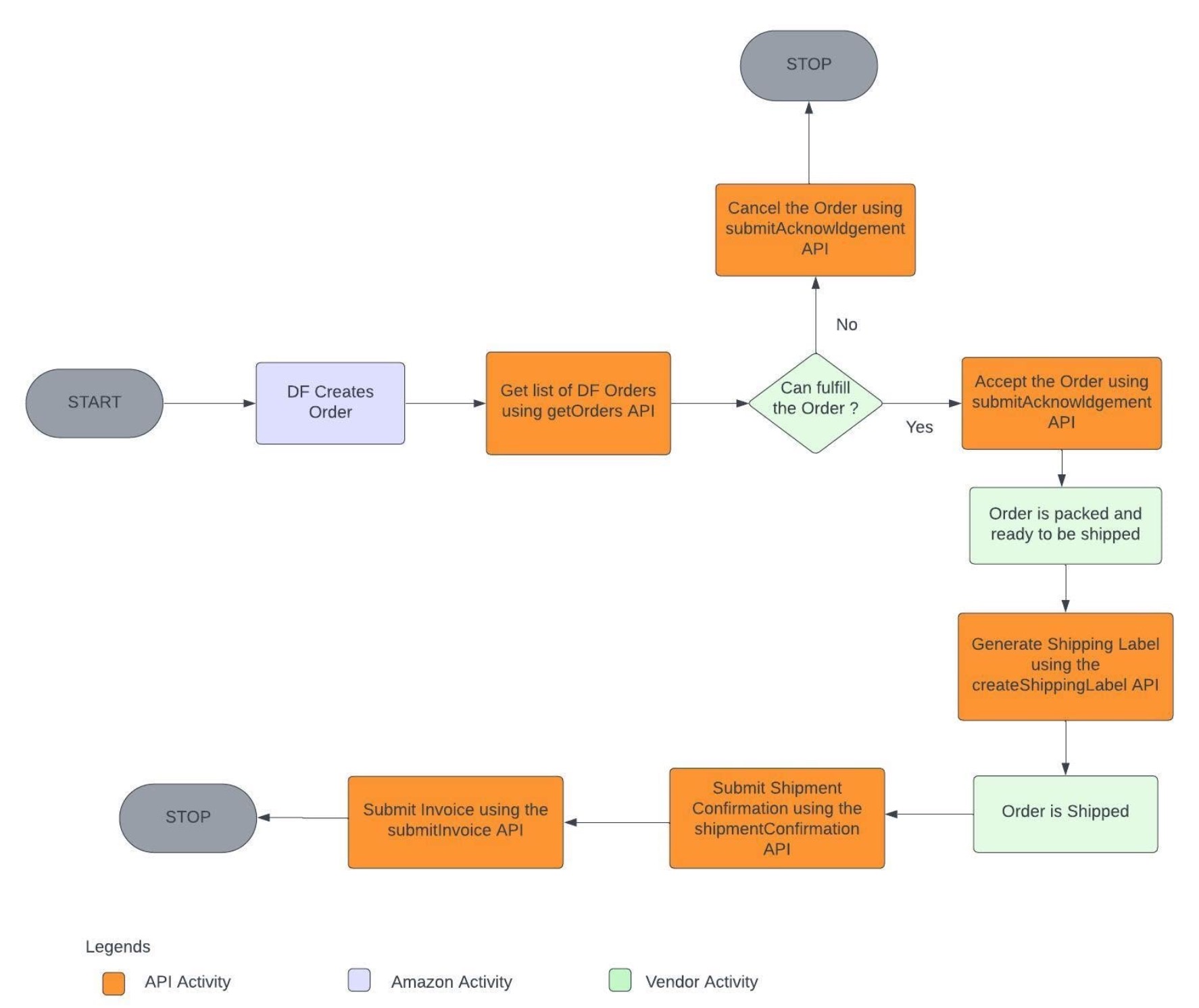
Key functions at a glance:
Order Processing: New Direct Fulfillment orders can be automatically retrieved and imported into your own ERP system, eliminating manual data entry.
Inventory Management: Stock levels can be regularly reported to Amazon via API. This keeps available quantities up-to-date, preventing stockouts and cancellations.
Shipping Processes: Shipping labels can be requested via API. The API also enables the automatic transmission of shipment confirmations, including tracking data, to Amazon. Packing slips and customer invoices can also be exchanged electronically.
Payment Processing: Invoices and credit memos can be created digitally and submitted to Amazon, speeding up the payment process and creating transparency.
This automation reduces the risk of manual entry errors and improves overall process efficiency. In practice, vendors can either develop their own integrations (e.g., via the Selling Partner API endpoints for Direct Fulfillment) or use middleware/EDI providers that support these APIs.
Direct Fulfillment EDI Dynamic Sandbox
For vendors using EDI connections, Amazon has introduced the Direct Fulfillment EDI Dynamic Sandbox. This dynamic test environment closely mimics the production DF-EDI environment, allowing for safe testing of workflows before going live. The only difference is that no real customer data is used.
The Ship Label Request (SL) and Ship Label Response (SLR) allow vendors to test the entire process of label retrieval and shipment confirmation realistically, without having to use real customer orders.
Both positive cases (correct workflows that result in a label) and negative cases (e.g., intentionally incorrect data to provoke error messages) can be tested. Negative tests provide controlled error messages, while successful tests return the expected label data.
By testing extensively in the Dynamic Sandbox, integration problems can be identified early before the system goes live. This minimizes surprises in real operation and facilitates seamless EDI integration for Direct Fulfillment.
Inventory and Catalog Management
Direct Fulfillment Inventory Cloning
To enable vendors to seamlessly use their existing product portfolio for Direct Fulfillment, Amazon provides Inventory Cloning. This involves copying (cloning) products from the regular vendor (retail) catalog to the Direct Fulfillment catalog. Specifically, a vendor’s ASINs are duplicated under a special DF vendor code, making them available for the direct-ship program.
During the cloning process, all current product data for the ASIN is adopted – including the terms (cost prices) at the time of cloning.
After cloning, the product exists twice: once in the normal vendor listing (for regular orders to an Amazon warehouse) and once in the Direct Fulfillment listing. Both initially share the same product information.
Vendors can set different costs for Direct Fulfillment after the product has been cloned. This allows for different terms for DF orders (e.g., due to different shipping cost structures).
The cloning process can take some time, depending on the volume. The status of the clone job can be viewed in Vendor Central (usually under Items > Direct Fulfillment Inventory). Once completed, the cloned items are available for Direct Fulfillment orders.
Inventory Cloning allows vendors to participate in the DF program without having to set up their products again, selling both via Amazon’s warehouse (FBA) and via direct shipping. It is important to maintain the inventory for the DF catalog just as you do for the regular inventory.
Shipping and Labeling
Shipping Label Formats
Amazon provides prepaid shipping labels for Direct Fulfillment orders, which the vendor must use. These labels can be generated in two formats.
PNG Format: An image file format that can be downloaded directly from Vendor Central and printed on standard printers. The labels are typically designed in a 6x4 inch (15 cm x 10 cm) format, suitable for common shipping label sizes. This format is ideal if the vendor does not own a thermal printer.
ZPL Format: A Zebra Programming Language format (essentially a text file with printer commands) optimized for thermal printers (label printers). Amazon usually offers the ZPL label in two resolutions - 203 dpi and 300 dpi. To use ZPL, you need a compatible thermal printer or software that can render ZPL files. The advantage is faster, more precise printing on continuous label rolls.
Both formats contain the same barcode and shipping information. The choice of format depends on the vendor’s equipment.
Performance Monitoring and Metrics
Amazon monitors the performance of Direct Fulfillment vendors using various metrics. These KPIs are crucial in determining whether a vendor is considered a reliable partner. Vendors can view their DF performance metrics in Vendor Central under Reports > Operational Performance or Direct Fulfillment Reports and should review them regularly.
Key Metrics and Their Purpose:
Cancellation Rate:
The percentage of DF orders canceled by the vendor. It usually increases when inventory levels are not updated correctly or frequently enough, leading to orders for out-of-stock items. The goal is to keep cancellations below a certain percentage – therefore, daily inventory updates and meticulous inventory management are essential.
Ship Method Mismatch:
This metric counts instances where the vendor used a different shipping method than the one specified by Amazon. Amazon expects shipments to always use the service indicated on the label (e.g., not unilaterally choosing a slower service). Deviations can lead to delays and are recorded negatively.
Delivery Estimated Accuracy (DEA):
Delivery Estimated Accuracy (DEA) measures whether orders actually arrive by the confirmed estimated delivery date. Any delivery delay reduces this rate. A high DEA (on-time delivery) is essential for customer satisfaction and avoids customer inquiries or complaints. Vendors should therefore ensure they can reliably meet shipping and delivery times–including by selecting appropriate shipping services.
Refunds & Replacements:
This indicator shows how often customers request refunds or replacements after receiving DF orders. Reasons can include damaged goods, incorrect items, or other problems. A low rate means the vendor is shipping the right products in perfect condition and that they match the description. Correct packaging and pre-shipment quality control also play a role here.
Other Metrics:
Amazon tracks other KPIs as well, such as the Late Shipment Rate (for shipments dispatched after the ExSD), the Carrier First Scan Rate (for shipments without a first scan within 24 hours), and the Scan Rate (the percentage of shipments with valid tracking info). All of these contribute to the overall picture of vendor performance.
Consequences of Poor Performance
If a vendor fails to meet the specified targets, Amazon will typically issue a warning first. A notification is sent requesting an analysis of the causes and a plan for corrective action. In cases of persistent violations (e.g., a consistently high cancellation or late shipment rate), Amazon can place the vendor’s account in the Direct Fulfillment program on at-risk status. In extreme cases, a temporary suspension may follow: This means Amazon sets the vendor’s DF inventory to zero, stops accepting new DF orders, and requires the vendor to submit a plan of action for remediation. Operations can only be resumed after Amazon’s approval. It is therefore in the vendor’s best interest to regularly monitor DF performance and proactively address problems to maintain a high-quality customer experience.
Data Protection and Compliance
Participation in the Direct Fulfillment program comes with strict requirements for handling customer data. Amazon has issued the Direct Fulfillment Data Protection Policy to ensure that vendors handle personal data responsibly.
Key requirements of the data protection policy include:
-
Data Deletion: All customer data received from Amazon may be stored for a maximum of 30 days, unless order processing requires an exception. In practice, this means that data such as customer addresses must be deleted or anonymized promptly after an order has been shipped and completed.
-
Incident Response: Vendors must maintain a written Incident Response Plan that is activated in the event of a security incident (e.g., data breach, hacking attack). Amazon must be notified within 48 hours of any such data security incident. This plan should name responsible individuals and outline measures for containment and communication.
-
Security Program: A documented security program must be implemented within the company, covering all aspects of data protection and IT security. This includes annual policy reviews, regular employee training on data security, and the appointment of a security officer. The program should meet at least industry-standard practices (e.g., ISO 27001/NIST).
-
Encryption: All data received from Amazon must be encrypted both in transit and at rest. This ensures that no plain text can be read even in the event of unauthorized access. Personally Identifiable Information (PII), in particular, must be protected by appropriate cryptography.
-
Monitoring and Logging: Vendors should ensure that security-relevant logs and access paths are reviewed regularly (at least weekly). Any anomalies or unauthorized access must be detected and investigated. The logs should be retained for at least 12 months to provide a history if needed.
-
“Amazon-Label-Only” Vendor: A key data protection measure in Direct Fulfillment is the “Amazon-Label-Only” approach. Vendors who work exclusively with shipping labels provided by Amazon (which is standard in the DF program) do not receive separate customer data through the usual channels. The customer’s name, address, and contact information appear only on the label and are not accessible in plain text in Vendor Central or via API/EDI. This practice ensures that customer data is visible only as long as necessary and only to the extent essential for shipping. For the vendor, this also means they are prohibited from storing the information from the label elsewhere and must use it exclusively for shipment processing.
These requirements serve to protect sensitive customer data and ensure that Amazon vendors adhere to security standards comparable to Amazon’s own. Amazon reserves the right to make audit requests or to demand proof that these measures are being implemented.
Conclusion
Amazon Direct Fulfillment enables vendors to handle Amazon orders independently, enhancing both delivery speed and control over the shipping process. By integrating APIs and EDI connections, vendors can automate many workflows, resulting in greater efficiency and fewer errors. At the same time, expectations for accurate inventory management, reliable logistics, and secure data handling rise significantly.
To succeed in the program, vendors must update inventory daily, ship on time, and meet Amazon’s strict performance standards. When guidelines are followed consistently – from packaging requirements and performance metrics to data protection – all parties benefit: vendors gain a scalable direct-shipping model, Amazon strengthens customer satisfaction, and end customers enjoy fast, dependable deliveries. Properly implemented, Direct Fulfillment becomes a true win-win within Amazon’s value chain.
FAQ
What is the difference between Direct Fulfillment and FBA?
With Fulfilled by Amazon (FBA), vendors store their products in Amazon’s logistics centers, and Amazon ships the orders. With Direct Fulfillment (DF), vendors ship directly from their own warehouse without intermediate storage at Amazon.
What are the requirements for participating in the DF program?
To participate in the Amazon Direct Fulfillment program, vendors need an active Vendor Central account, their own warehouse with functioning shipping processes, and the ability to submit daily inventory updates to Amazon. In addition, shipping policies must be followed, including on-time shipping, correct labeling, and appropriate packaging standards.
Who is Direct Fulfillment suitable for?
Direct Fulfillment is particularly suitable for vendors with stable logistics and robust IT integration, especially for fast-moving or seasonal products, as well as for manufacturers who want to quickly test new items on the market. In contrast, those with irregular inventory levels or who cannot utilize a technical connection via APIs usually benefit more from the classic vendor model or FBA.
Subscribe to Newsletter
Get the latest Amazon tips and updates delivered to your inbox.
We respect your privacy. Unsubscribe anytime.
